20201210 Viral load in patients with covid-19 has been shown to be greater in those with more severe illness. 20210107 Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay paper or report.
 Factors Affecting Stability And Infectivity Of Sars Cov 2 Journal Of Hospital Infection
Factors Affecting Stability And Infectivity Of Sars Cov 2 Journal Of Hospital Infection
20200421 The virus causing COVID-19 disease severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2 is highly infectious and the initial dose could be related to the severity.
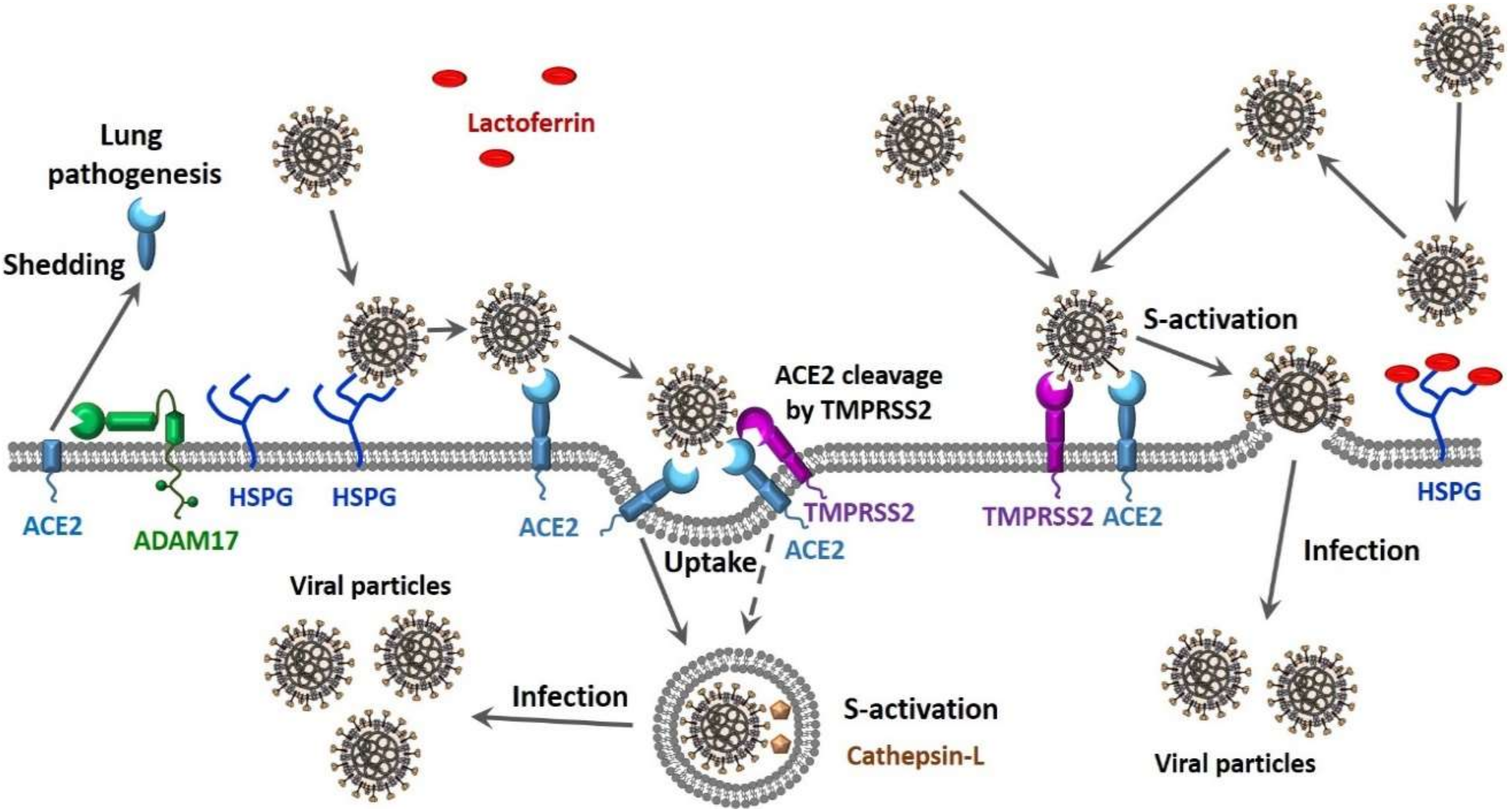
Does viral load affect covid severity. Aerosol transmission seemed to raise the risk of more severe respiratory tract complications Immune response can be considered an ordered process that happens in stages. 20200330 A study on COVID-19 patients in China links high viral load to worse symptoms Viral load is the amount of a virus inside someones body during infection People can try. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in saliva may be linked to COVID.
Our best belief is that the viral load and transmission peaks relatively early in the course of symptomatic disease and that by day 8 or 9 transmission risk is rapidly approaching baseline. 20201101 Higher viral load measures did not reflect COVID-19 severity. 20200401 Overall our data indicate that similar to SARS in 200203 patients with severe COVID-19 tend to have a high viral load and a long virus-shedding period say researchers.
20200327 However in the case of covid-19 it doesnt necessarily follow that a higher viral load will lead to more severe symptoms. Amount of particles or viral load affect severity Professor Lucy Yardley from the University of Bristol sounded the alarm today saying evidence shows viral load plays a big role in how sick someone will become. 1 Viral load in COVID-19 might correlate with infectivity disease phenotype morbidity and mortality.
For instance health workers investigating the covid-19 outbreak in the. As of February 11 2021 Maccabi Healthcare Services MHS in Israel has vaccinated. 20200918 While there is some emerging research that viral inoculum may play a role in disease severity in COVID-19 other infectious disease specialists have explored how viral load -- the amount of viral.
20200506 Dr Wei and colleagues added that high viral load also seemed to raise the risk of a serious illness in patients with SARS a similar virus that caused an. 20210329 However the effect of vaccination on viral load in COVID-19 post-vaccination infections is currently unknown 8. Not much is.
Pulmonary medicine specialist and. 20200403 Much of COVID-19s prevalence severity and lethality may have to do with viral particles you are exposed tothe issue of viral load also called viral dose. 20201125 The most important take-home message is that a positive COVID-19 test by any method does not correspond to the presence of a viable virus.
20210210 Viral abundance could drop further after the vaccines second dose Cyrille Cohen a vaccine expert at Bar-Ilan University who advises Israels health ministry on COVID-19 vaccines and wasnt involved with the study tells The Times of Israel. 20201030 Across the spectrum of viral infections the extent of viral load has been a predictor of disease severity and progression including for HIV 1718. 20210112 Pulmonary medicine specialist Dr Mike Hansen explains how viral load is a potential indicator for severity of illness in COVID-19 patients.
20200806 However technology based on RT-PCR allows for calculation of viral load which is associated with transmission risk and disease severity in other viral illnesses. 20200813 In some studies it has been observed that the prevalence and severity of COVID19 infection have an association with the viral load of SARSCoV2 as determined from the sputum and nasopharyngeal swab NPS. If someone gets infected by a droplet containing a high load of the SARS-CoV-2 virus would he be more likely to develop more severe symptoms compared to someone who gets infected by a.
Based on their findings the team recommends that the viral load of COVID-19 might be a useful marker for assessing disease severity and prognosis.
 Correlation Between Relative Nasopharyngeal Virus Rna Load And Lymphocyte Count Disease Severity In Patients With Covid 19 Viral Immunology
Correlation Between Relative Nasopharyngeal Virus Rna Load And Lymphocyte Count Disease Severity In Patients With Covid 19 Viral Immunology
 Biomarkers For Predicting Covid 19 Disease Severity Drug Target Review
Biomarkers For Predicting Covid 19 Disease Severity Drug Target Review
 Inhaled Corticosteroids And Covid 19 A Systematic Review And Clinical Perspective European Respiratory Society
Inhaled Corticosteroids And Covid 19 A Systematic Review And Clinical Perspective European Respiratory Society
 Biomolecules Free Full Text Why Covid 19 Transmission Is More Efficient And Aggressive Than Viral Transmission In Previous Coronavirus Epidemics Html
Biomolecules Free Full Text Why Covid 19 Transmission Is More Efficient And Aggressive Than Viral Transmission In Previous Coronavirus Epidemics Html
 New Covid Variant Does Not Cause More Severe Illness Study Shows Financial Times
New Covid Variant Does Not Cause More Severe Illness Study Shows Financial Times
 Rationale For Azithromycin In Covid 19 An Overview Of Existing Evidence Bmj Open Respiratory Research
Rationale For Azithromycin In Covid 19 An Overview Of Existing Evidence Bmj Open Respiratory Research
Covid 19 And Sars Cov 2 Immune Response Mechanistic Insights World Allergy Organization
 Correspondence Between Development Of Viral Load During Severe Acute Download Scientific Diagram
Correspondence Between Development Of Viral Load During Severe Acute Download Scientific Diagram
 Correlation Between Relative Nasopharyngeal Virus Rna Load And Lymphocyte Count Disease Severity In Patients With Covid 19 Viral Immunology
Correlation Between Relative Nasopharyngeal Virus Rna Load And Lymphocyte Count Disease Severity In Patients With Covid 19 Viral Immunology
 Air Pollution By No 2 And Pm 2 5 Explains Covid 19 Infection Severity By Overexpression Of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 In Respiratory Cells A Review Springerlink
Air Pollution By No 2 And Pm 2 5 Explains Covid 19 Infection Severity By Overexpression Of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 In Respiratory Cells A Review Springerlink
 How Does Sars Cov 2 Targets The Elderly Patients A Review On Potential Mechanisms Increasing Disease Severity European Journal Of Internal Medicine
How Does Sars Cov 2 Targets The Elderly Patients A Review On Potential Mechanisms Increasing Disease Severity European Journal Of Internal Medicine
 New Study Shows Sars Cov 2 Viral Load Peaks In The Early Stages Of Disease
New Study Shows Sars Cov 2 Viral Load Peaks In The Early Stages Of Disease
 Sars Cov 2 Viral Load And Severity Of Covid 19 Studied Healthcare Purchasing News
Sars Cov 2 Viral Load And Severity Of Covid 19 Studied Healthcare Purchasing News
 Factors Of Severity In Patients With Covid 19 Cytokine Chemokine Concentrations Viral Load And Antibody Responses In The American Journal Of Tropical Medicine And Hygiene Volume 103 Issue 6 2020
Factors Of Severity In Patients With Covid 19 Cytokine Chemokine Concentrations Viral Load And Antibody Responses In The American Journal Of Tropical Medicine And Hygiene Volume 103 Issue 6 2020
 How Much Of The Coronavirus Does It Take To Make You Sick Stat
How Much Of The Coronavirus Does It Take To Make You Sick Stat
 Air Pollution By No 2 And Pm 2 5 Explains Covid 19 Infection Severity By Overexpression Of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 In Respiratory Cells A Review Springerlink
Air Pollution By No 2 And Pm 2 5 Explains Covid 19 Infection Severity By Overexpression Of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 In Respiratory Cells A Review Springerlink
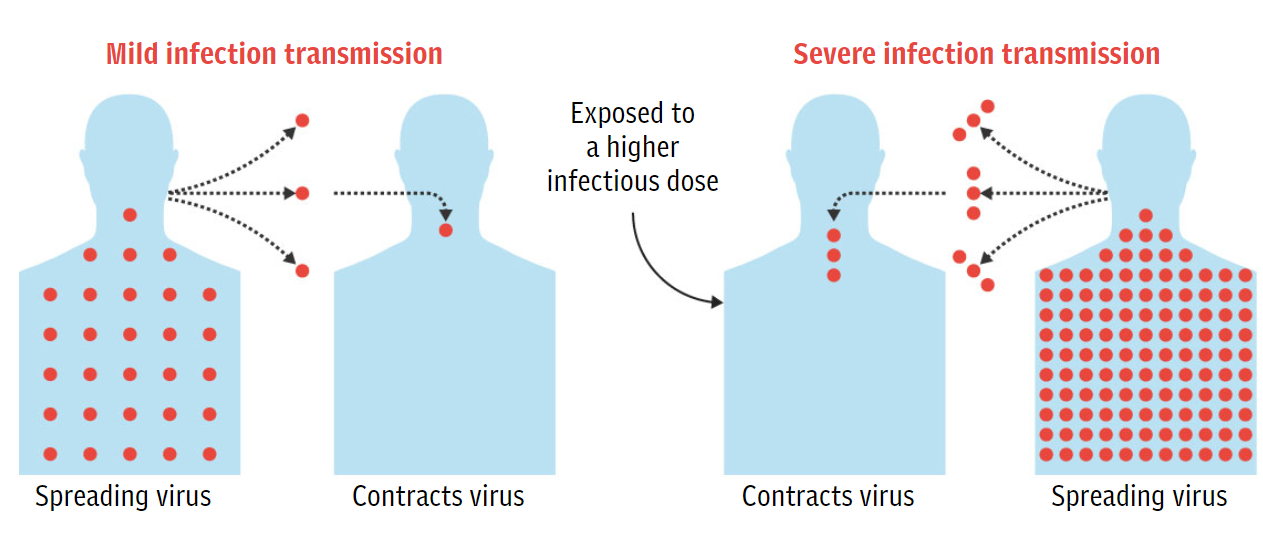 The Viral Load The X Factor Predicting Disease Severity In Covid 19 By Doctor Yak The Yak Medium
The Viral Load The X Factor Predicting Disease Severity In Covid 19 By Doctor Yak The Yak Medium
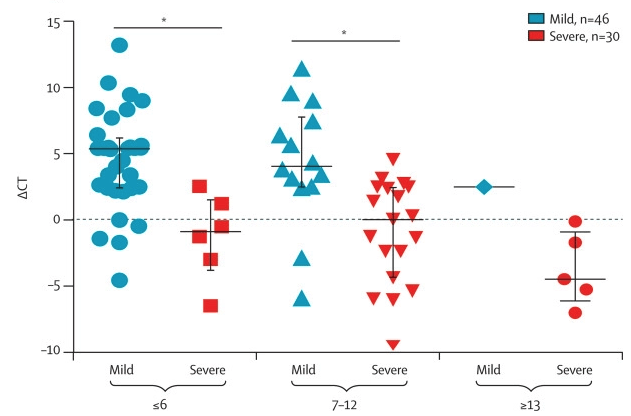 Viral Dynamics Mild Vs Severe Covid 19 Immunopaedia
Viral Dynamics Mild Vs Severe Covid 19 Immunopaedia
 Role Of Favipiravir In The Treatment Of Covid 19 International Journal Of Infectious Diseases
Role Of Favipiravir In The Treatment Of Covid 19 International Journal Of Infectious Diseases