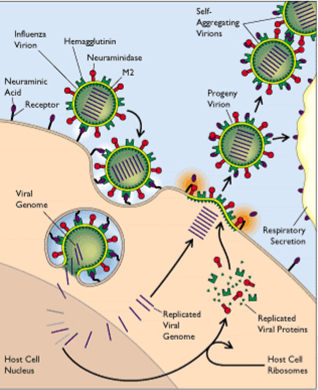
Therefore viruses are very difficult to treat. Viruses use the host cells machinery to make lots of copies so many that the cell bursts and infects other cells around it.
 Virus Release An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Virus Release An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
20200324 When the new virus particles are complete the virus needs a way to release them to infect more cells.

Does viruses kill host cells. Once it enters a liver cell viral proteins and more virus are just secreted into the serum of patients for the duration of that cells lifetime. It is important to clarify that when a virus infects a human it does not always end up in a disease. HBV is non-cytopathic and doesnt kill the cell.
20180501 Viruses hijack healthy host cells exploiting resources and reproductive machinery for rapid replication. Viruses can have a lytic killing the host cell and lysogenic not killing the host cell phase. Viruses on their own are not alive but they can act as if they are once they reach your bodys cells.
The causes of death include cell lysis alterations to. 20201113 Infected cells can be damaged or die while hosting a virus. So Im studying basic virology for uni and a question came to my mind.
20210308 These viruses do not usually kill the host cell and are known as cytopathic viruses. The virus does not immediately kill a host cell The injected viral DNA integrates into a host chromosome and remains harmless for a period of time sometimes years It becomes harmful later when it enters the lytic cycle ex. Virus attachment to host cells is similarly reversible at least in its primary step.
Virus persists for decades in the same cell. First they simply kill the host cell by breaking open the host cell. Its a matter of debate whether any auto-immune diseases are related to lysogenic viruseses.
Some viruses cause no apparent. Therefore it is referred to as an intracellular parasite. There are two ways that the viruses break out of the host cell.
Viruses often kill host cells which is where the sick feeling comes from. 20141027 In the lytic cycle the virus focuses on reproduction. 20200416 Viruses infect organisms in each of the six kingdoms of life inserting their own genetic material into host cells genetic material and directing the cells to.
Distilled water at 0C. Influence A virus is an example of a cytopathic virus. Once replication has been completed and the host cell is exhausted of all resources in making viral progeny the viruses may begin to leave the cell by several methods1 The term is used to refer to shedding.
Some only do one or the other. The infection occurs when the virus begins to multiply. When enveloped viruses leave the host cell they leave it kind of intact considering that other kinds of viruses lisate it except for a tiny section of membrane.
Can produce almost complete liberation of T2 virus. Viruses are typically an RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protective protein coat. Most viral infections eventually result in the death of the host cell.
However a major consequence of speedy reproduction is the increased risk of random genetic mutation which can result in a myriad of unique viral strains. It invades a cell inserts its DNA and creates thousands of copies of itself bursts through the cell membrane killing the cell and each new viral strand invades new cells replicating the process. 20210314 As the virus gets into the body it changes metabolic processes to introduce more viral particles.
They take over normal cell functions and force cells to make more viruses. The causes of death include cell lysis alterations to the cells surface membrane and various modes of programmed cell death. This can happen through replication of the host cell or even by infecting our DNA.
Lytic viruses simply burst out releasing all their virions in one huge pop and killing the cell in the process. Lysogenic viruses release new virions one by one allowing the host cell to survive and reproduce. And the disease occurs when many body cells are damaged by the infection which is also when the symptoms and illness appear.
The second way is by pinching out from the cell membrane and break away budding with a piece of the cell membrane surrounding them. Viral shedding refers to the expulsion and release of virus progeny following successful reproduction during a host-cell infection. Viruses infect our body and invade our cells.
Most viral infections eventually result in the death of the host cell. 20150526 They survive by inserting their DNA into the DNA of host cells so that instead of making proteins for the cells the cell machinery makes virus proteins and copies of the virus. They get inside the hosts cells and take it over.
Viral replication and disease pathogenicity. Viruses take any chance they can to find a host. Even lysogenic viruses can be an issue since they can set off the immune system on a regular basis.
20210128 Viruses cannot reproduce by itself because of this it relies on the host cellular machinery to do so. 20100406 The range of structural and biochemical ie cytopathic effects that viruses have on the host cell is extensive.
 Steps Of Virus Infections Text Version Biology For Majors Ii
Steps Of Virus Infections Text Version Biology For Majors Ii
 How Do Viruses Invade And Exploit Healthy Cells
How Do Viruses Invade And Exploit Healthy Cells
 Pin On Https Drawittoknowit Com
Pin On Https Drawittoknowit Com
 The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology
The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology
 Viruses Hijack Living Host Cells And Then Replicate Themselves
Viruses Hijack Living Host Cells And Then Replicate Themselves
 Pin On Learning Science For Kids
Pin On Learning Science For Kids
 Pin On Health And Medicine Illustrated
Pin On Health And Medicine Illustrated
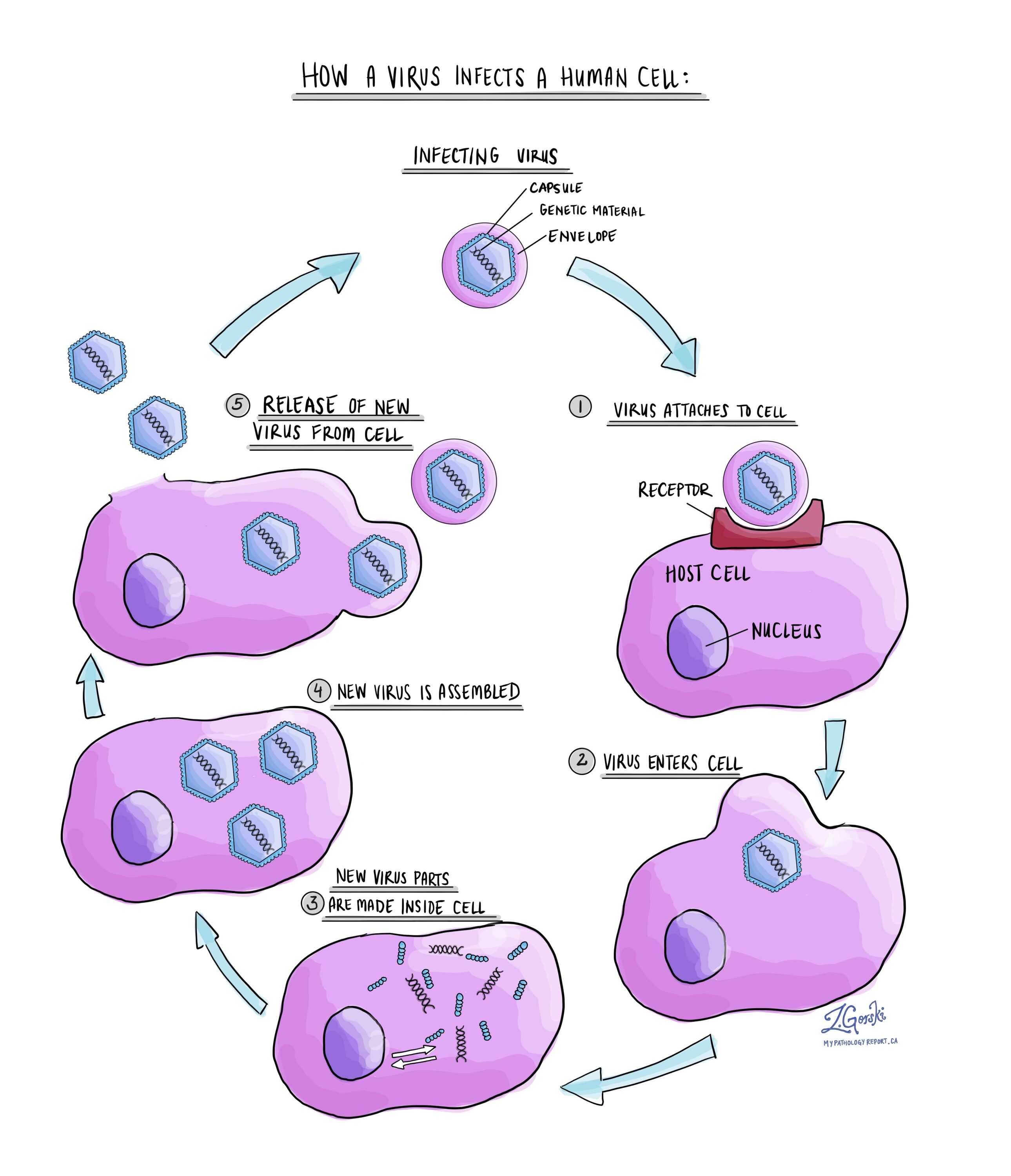 Virus Pathology Dictionary Mypathologyreport Ca
Virus Pathology Dictionary Mypathologyreport Ca
 Virus Infections And Hosts Biology For Majors Ii
Virus Infections And Hosts Biology For Majors Ii
 Virus The Cycle Of Infection Britannica
Virus The Cycle Of Infection Britannica
Structure Of Viruses Microbiology Master
 Virus Replication British Society For Immunology
Virus Replication British Society For Immunology
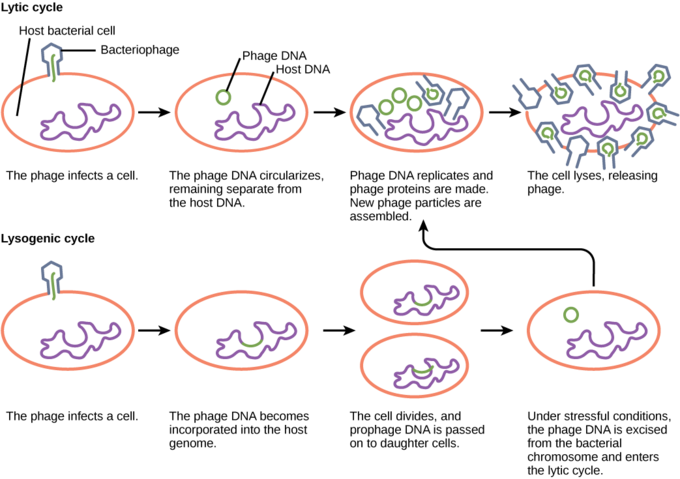 Virus Infections And Hosts Boundless Biology
Virus Infections And Hosts Boundless Biology
 Virus Infections And Hosts Biology For Majors Ii
Virus Infections And Hosts Biology For Majors Ii